Defining Mental Health Crisis Intervention
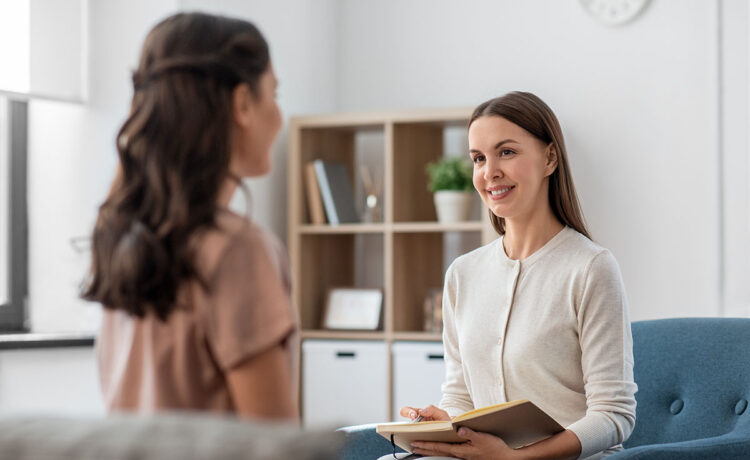
Mental health crisis intervention is a critical process that provides immediate support to individuals experiencing severe emotional distress or mental health emergencies. It aims to stabilize the situation and prevent harm, offering a lifeline to those in dire need. Crisis intervention therapy offers immediate relief and coping strategies for individuals experiencing overwhelming emotions and stress, helping them regain normal functioning. Crisis intervention therapy offers immediate relief and coping strategies for individuals experiencing overwhelming emotions and stress, helping them regain normal functioning..
Historical Development of Crisis Intervention
The concept of crisis intervention has evolved significantly since its inception. It began in the 1960s, when Gerald Caplan introduced the crisis intervention theory, emphasizing the need for timely and effective responses to mental health emergencies. Over the decades, this approach has expanded to include a variety of services, from 24/7 hotlines to mobile response teams, ensuring that help is available whenever and wherever it is needed.
Key Principles of Effective Intervention
Effective mental health crisis intervention hinges on several key principles. One of the most important is accessibility—ensuring that individuals can receive help without long waits. This immediacy is crucial in preventing crises from escalating. Additionally, interventions must be culturally sensitive and trauma-informed, recognizing the unique backgrounds and experiences of each person. By integrating these principles, crisis intervention programs can provide comprehensive support that not only addresses the immediate crisis but also sets the stage for long-term recovery and well-being.
Components of Successful Crisis Intervention Programs
Role of Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals are the backbone of crisis intervention programs. With their specialized knowledge and skills, they provide critical support during emergencies, helping individuals navigate through their most challenging moments. These professionals, including psychologists, psychiatrists, and social workers, work tirelessly to assess, diagnose, and offer immediate care. Their expertise ensures that individuals receive the appropriate intervention and support needed to stabilize and recover. At Evoke Wellness, the emphasis is on employing highly trained staff who are equipped to handle a variety of mental health crises, ensuring comprehensive care for all individuals.
Importance of Community Resources
Community resources play a vital role in enhancing the effectiveness of crisis intervention programs. By leveraging local resources, these programs can offer a more holistic approach to care, addressing not just the immediate crisis but also the underlying factors contributing to it. This includes access to housing, food, and employment services, which are crucial for long-term recovery. Evoke Wellness collaborates with community organizations to ensure that individuals have access to the necessary resources, fostering a supportive environment that promotes healing and growth.
Integration of Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity is an essential component of successful crisis intervention programs at places like Serenity at Summit. Understanding and respecting the cultural backgrounds of individuals in crisis can significantly impact the effectiveness of the intervention. Crisis teams that incorporate cultural awareness into their practice are better equipped to communicate and connect with individuals, building trust and rapport. At Evoke Wellness, there is a strong commitment to cultural competence, ensuring that all interventions are respectful and inclusive of diverse cultural perspectives, ultimately leading to more effective and personalized care.
The Impact of Crisis Intervention on Individuals and Communities
Transforming Lives Through Immediate Support
Crisis intervention programs are like a safety net for people teetering on the edge. Imagine someone feeling overwhelmed by anxiety or haunted by past traumas. These programs step in during such critical moments, offering immediate support that can literally change the course of a person’s life. The immediate intervention provided by these programs can be the difference between life and death. They offer not just a lifeline but also a way to stabilize someone’s situation, preventing further deterioration. This immediate support helps individuals regain control and sets them on a path to recovery.
Building Stronger Community Relationships
Crisis intervention doesn’t just aid individuals; it strengthens community bonds too. When mental health professionals, law enforcement, and community resources work together, it fosters trust and cooperation among them. This collaboration ensures that individuals in crisis receive comprehensive care, reducing the need for emergency room visits and easing the burden on healthcare systems. Moreover, crisis intervention programs are effectively reducing the need for emergency room visits during mental health crises while simultaneously strengthening relationships between police and communities. This collaborative approach not only resolves immediate crises but also builds a more cohesive and resilient community.
Reducing Stigma Around Mental Health
One of the most significant impacts of crisis intervention programs is their role in reducing the stigma associated with mental health issues. By providing timely and compassionate care, these programs normalize conversations around mental health and encourage individuals to seek help without fear of judgment. As more people see mental health crises being addressed openly and effectively, it helps break down barriers and misconceptions. This shift in perception is crucial for creating an environment where mental health is treated with the same importance as physical health, leading to a more understanding and supportive society.
Training and Development for Crisis Intervention Teams
Essential Skills for Crisis Responders
Crisis intervention teams are the backbone of mental health emergency responses, and their training is pivotal to their effectiveness. These teams must be adept at really listening and showing empathy, crucial skills that help in calming tense situations. Understanding trauma responses and being sensitive to cultural differences are also vital. Modern training programs focus on these areas to ensure that responders can adapt their approach to the unique needs of each individual. The Addiction Center plays a significant role in equipping responders with the necessary skills to handle situations involving substance abuse, which often complicates mental health crises.
Ongoing Education and Certification
Continuous learning is key in the ever-evolving field of crisis intervention. Regular participation in workshops and seminars keeps responders updated on the latest techniques and best practices. Certifications like those from the Addiction Center provide credibility and ensure that teams are using the most current, evidence-based approaches. Online courses have become popular, allowing professionals to balance their busy schedules while staying informed. This ongoing education is not just about maintaining certifications; it’s about improving the quality of support provided to those in crisis.
Adapting to Diverse Crisis Scenarios
Every crisis is unique, and responders must be prepared to handle a wide range of scenarios. Training often includes role-playing and scenario-based exercises that mimic real-life situations. This hands-on approach helps responders develop the flexibility needed to adjust their strategies on the fly. Special attention is given to dealing with specific groups, such as young people, older adults, veterans, and individuals facing multiple challenges. By understanding the distinct needs of these groups, crisis teams can offer more tailored and effective support. The Addiction Center’s expertise in handling addiction-related crises is an invaluable resource in these training programs, ensuring that responders are well-prepared for any situation they might encounter.
Crisis Intervention Techniques and Strategies
De-escalation Methods
In the heat of a mental health crisis, keeping things from boiling over is essential. De-escalation methods focus on calming the person in crisis and stabilizing the situation. This involves using a calm voice, maintaining a non-threatening posture, and showing empathy. It’s about making the person feel heard and safe, reducing the immediate tension. These strategies require patience and practice, often involving both verbal and non-verbal communication techniques to gently guide the individual towards a more peaceful state.
Safety Planning and Risk Assessment
Safety planning and risk assessment are critical components of crisis intervention. These strategies involve identifying potential risks and creating a plan to ensure the safety of the individual in crisis and those around them. It’s about understanding the signs that might indicate escalating danger and having a clear plan to address these risks. By assessing the situation thoroughly, responders can tailor their approach to meet the specific needs of the individual, ensuring that immediate threats are addressed and longer-term safety is considered.
Resource Mobilization and Follow-up
Resource mobilization is about connecting individuals in crisis with the appropriate support services. This could involve reaching out to mental health professionals, community resources, or emergency services, depending on the situation. Follow-up is equally important, as it ensures that the individual continues to receive support after the initial crisis has been managed. It’s not just about the immediate response; it’s about building a network of support that can help the person move forward. The Addiction Rehab Group, for example, plays a vital role in providing ongoing support and resources, ensuring that individuals have access to the help they need to recover and thrive.
Challenges and Solutions in Crisis Intervention
Addressing Barriers to Access
One of the biggest hurdles in mental health crisis intervention is making sure everyone can get help when they need it. Access to services can be uneven, often depending on where someone lives or what resources they have. Urban areas might have more facilities, but rural communities often struggle with fewer options. Harmony Ridge, for example, has been working hard to bridge these gaps by using mobile units and telehealth services to reach those in remote locations. This approach helps ensure that geographical barriers don’t prevent people from receiving timely intervention.
Improving Response Times
When a crisis hits, every second counts. Slow response times can mean the difference between life and death. Crisis teams are constantly working to improve how quickly they can get to someone in need. This involves better coordination among emergency responders, mental health professionals, and community resources. Harmony Ridge’s initiative to train local volunteers as first responders is one way to speed things up. By having trained individuals nearby, they can offer immediate support until professional help arrives.
Ensuring Long-term Support
Crisis intervention isn’t just about handling the immediate situation; it’s also about what happens next. Long-term support is crucial for recovery and preventing future crises. However, many programs face challenges in providing ongoing care due to limited funding and resources. Harmony Ridge tackles this by partnering with local organizations to create a network of support that includes follow-up care, counseling, and community programs. This network helps individuals transition from crisis to stability, ensuring that they aren’t left to navigate their recovery alone.
Measuring the Success of Crisis Intervention Programs
Quantitative Metrics and Data Analysis
Crisis intervention programs are increasingly relying on numbers to tell their story. By focusing on quantitative metrics, these programs can track their effectiveness over time. For instance, they often measure response times, the number of crises resolved without escalation, and the frequency of repeat crises. This data is crucial for understanding what’s working and what needs improvement. Numbers don’t lie, and they provide a clear picture of a program’s impact. However, it’s not just about collecting data; it’s about using it to make informed decisions that enhance service delivery.
Qualitative Success Stories
While numbers are essential, the real heart of crisis intervention programs lies in personal stories. These narratives provide insight into the human side of intervention. Success stories from individuals who have been helped by these programs often highlight the immediate and transformative impact on their lives. They also serve to inspire and motivate the professionals involved, reminding them of the importance of their work. These stories are powerful tools for advocacy and can help to build public support and understanding of mental health issues.
Continuous Improvement and Feedback
Continuous improvement is a cornerstone of successful crisis intervention programs. By incorporating feedback from both participants and professionals, these programs can adapt and evolve. Regular training updates and the integration of new techniques ensure that responders are prepared for any situation. Feedback loops are established to gather insights from every intervention, allowing for adjustments that improve outcomes. This process of ongoing evaluation and adaptation is essential for maintaining the effectiveness and relevance of crisis intervention efforts.
Collaborative Approaches in Crisis Intervention
Partnerships with Law Enforcement
In the realm of crisis intervention, partnerships with law enforcement are a cornerstone. Police officers often find themselves on the front lines of mental health crises. By teaming up with mental health professionals, they enhance their capacity to respond effectively. The Crisis Intervention Team (CIT) model exemplifies this collaboration, providing officers with specialized training to handle these situations with care and understanding. Such partnerships not only improve immediate responses but also foster trust between law enforcement and the communities they serve.
Involvement of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a vital role in crisis intervention by offering medical and psychological expertise. Their involvement ensures that individuals in crisis receive comprehensive care that addresses both physical and mental health needs. By working closely with crisis teams, healthcare professionals can help tailor interventions to each individual’s circumstances, creating a seamless continuum of care that extends beyond the initial emergency.
Engagement with Social Services
Social services are integral to crisis intervention strategies, offering essential support that addresses the broader social determinants of health. These services help connect individuals to resources that can stabilize their situations long-term, such as housing, employment assistance, and community support networks. By engaging with social services, crisis intervention programs can provide holistic support that not only resolves the immediate crisis but also lays the groundwork for sustained recovery and well-being.
Incorporating these collaborative approaches into crisis intervention not only enhances the effectiveness of immediate responses but also contributes to lasting positive outcomes for individuals and communities. For instance, frameworks like CAMS are designed to address complex issues such as suicide by fostering hope and reducing suicidal thoughts, demonstrating the power of integrated, collaborative efforts in mental health crisis intervention.
Future Directions for Mental Health Crisis Intervention
Innovations in Crisis Response
The future of mental health crisis intervention is leaning heavily on technological advancements. Sandstone Addiction Care is at the forefront of integrating digital tools into traditional crisis response frameworks. This integration allows for more immediate and tailored support, even in remote locations. Virtual reality therapy and AI-driven platforms are being explored to provide real-time assistance and predictive analysis for crisis situations.
Expanding Access to Services
One of the biggest challenges in mental health care is ensuring that help is available when and where it’s needed. Future strategies are focusing on expanding access through mobile units and telehealth services. Sandstone Addiction Care is among those leading the charge, offering 24/7 access to mental health professionals via digital platforms. This approach not only broadens reach but also reduces the stigma associated with seeking help.
Policy and Funding Considerations
For these advancements to be sustainable, significant policy shifts and funding allocations are necessary. Advocates are pushing for legislation that supports mental health crisis intervention as a critical component of public health. Sandstone Addiction Care is actively involved in lobbying for these changes, highlighting the need for comprehensive funding models that encompass both immediate crisis intervention and long-term mental health support. The focus is on creating a robust network of services that can adapt to the evolving needs of communities.